The current situation on board paper production
From 2009, China has become the largest papermaking country in the world.
In 2016, paper and paper board production and consumption reached more than 100 million tons. The ratios of different types of consumed paper are shown in the figure. Cardboard paper and corrugated board take up the most proportions. It’s mainly because of the great increase in express service. The ratio of newsprint has reduced to 3%, with a further declining trend. Other printing paper and household paper also take large proportions.
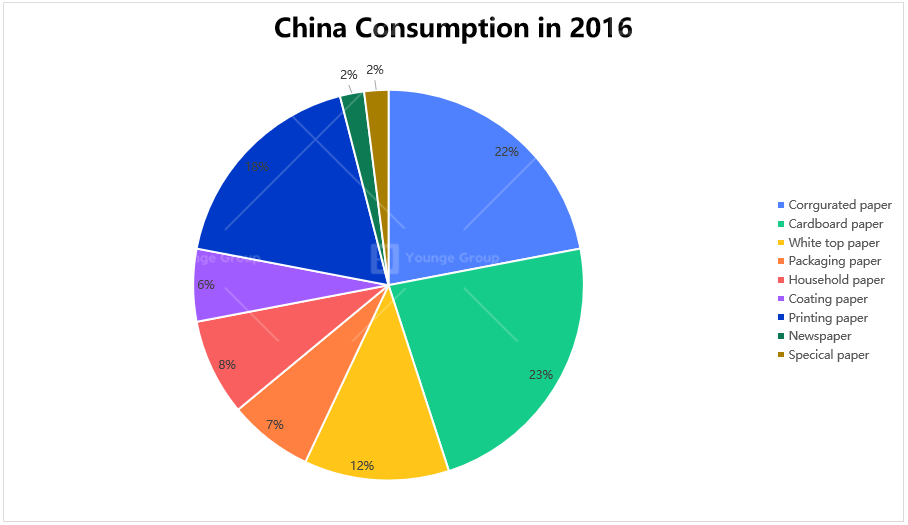
The pulping output in China has reached 79.25million tons and The consumption had reached 97.97 million tons.
Pulp category
The pulp can generally be categorized into 3 categories: wood pulp, waste paper pulp, and non-wood pulp.
- Wood pulp
Wood pulp is a virgin (or primary) fiber derived from harvested softwood or hardwood trees that are specifically grown for papermaking.
Consmption:29% (19% imported +10% produced in China)
- Waste paper pulp
Wood pulp is a virgin (or primary) fiber derived from harvested softwood or hardwood trees that are specifically grown for papermaking.
Consmption:65%
- Non-wood pulp
Non-wood fibers are defined as non-woody cellulosic plant materials from which papermaking fibers can be extracted. The most widely used non-woods for papermaking are straws, bagasse, bamboo, hemp, kenaf, jute, sisal, abaca, cotton inters (short fibers left after ginning), and reeds.
Consmption:6%
Different papers(or products) require different pulp
- Newsprint (newspaper), books, and periodicals— mechanical pulp, to improve the transparency of paper;
- High-grade printing paper—chemical pulp, to improve the strength of paper;
- Money paper-cotton pulp (linters), with good strength and folding resistance.
- Chemical fiber—dissolving pulp, with high cellulose content and good reactivity.
Pulping Technologies
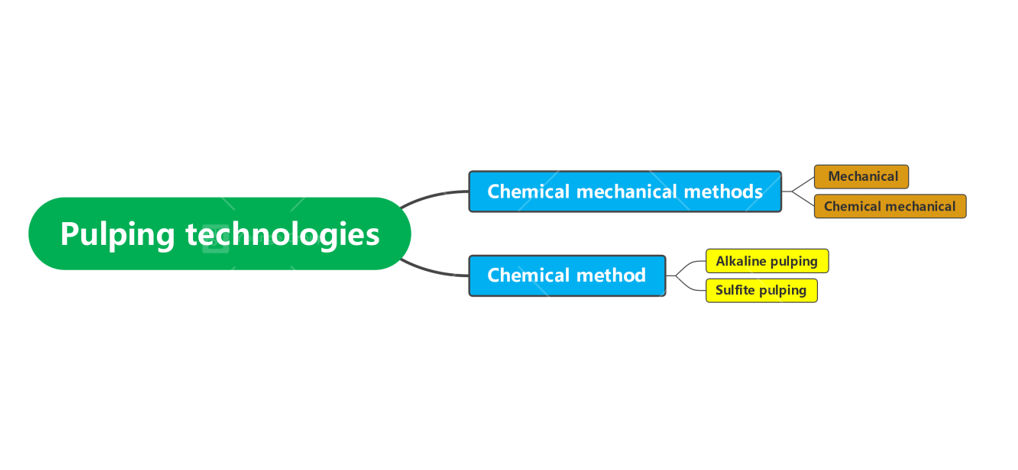
Chemical mechanical methods
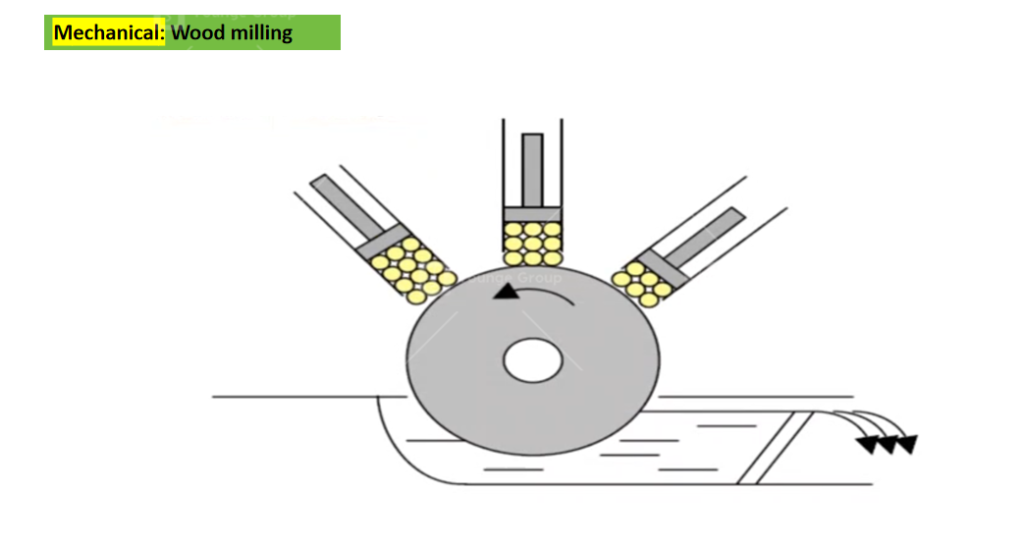
- Mechanical method: Wood milling is rubbing the surface of wood with stone, after being heated, the lignin, as the main content of the fiber cell, will be softened and turn into pulping after milling.
- The mechanical pulping processes use wood in the form of logs or chips that are mechanically processed, by grinding stones (from logs) or in refiners (from chips), to separate the fibers.The total yield is about 90%–98%. Lignin is retained in the pulp; therefore, high yields of pulp are obtained from wood.
- Mechanical pulps are characterized by high yield, high bulk, high stiffness, and low cost. They have low strength because the lignin interferes with hydrogen bonding between fibers when paper is made. The lignin also causes the pulp to turn yellow with exposure to air and light.
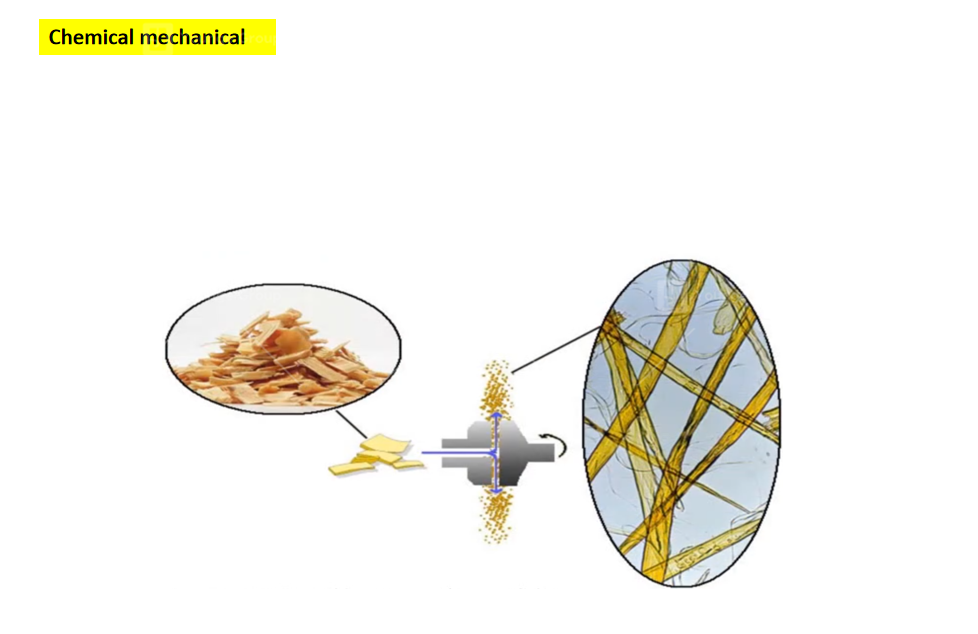
- Chemical mechanical pulping :after chemical treatment, the fiber becomes pulping after mechanical grinding.
- The raw materials from the preparation area are cleaned and pre-steamed by a scrubber, and then screw pressed and chemically pre-impregnated. The conveying equipment sends the extrusion impregnation stage, and the resulting pulp is sent to the second stage of impregnation. The impregnated pulp is sent to a two-stage disc refiner, and the final pulp from the pulp separator reaches the intermediate pool. After extrusion dehydration, secondary pulping and screening, the finished pulp is finally formed.
- The chemical treatment conditions are mild, and more lignin is retained in the pulp, and the pure pulp yield can be as high as 85/90. The properties of chemical mechanical pulp made from hardwood are similar to those of softwood pulp. The paper is dense, low in opacity, has a high content of long fibers, few fiber bundles, and good printing suitability. Chemical mechanical pulp can be made into newsprint, printing paper, cardboard, etc.
Chemical method
Chemical pulp breaks the bond between fibers by chemical processes to separate them into pulp.
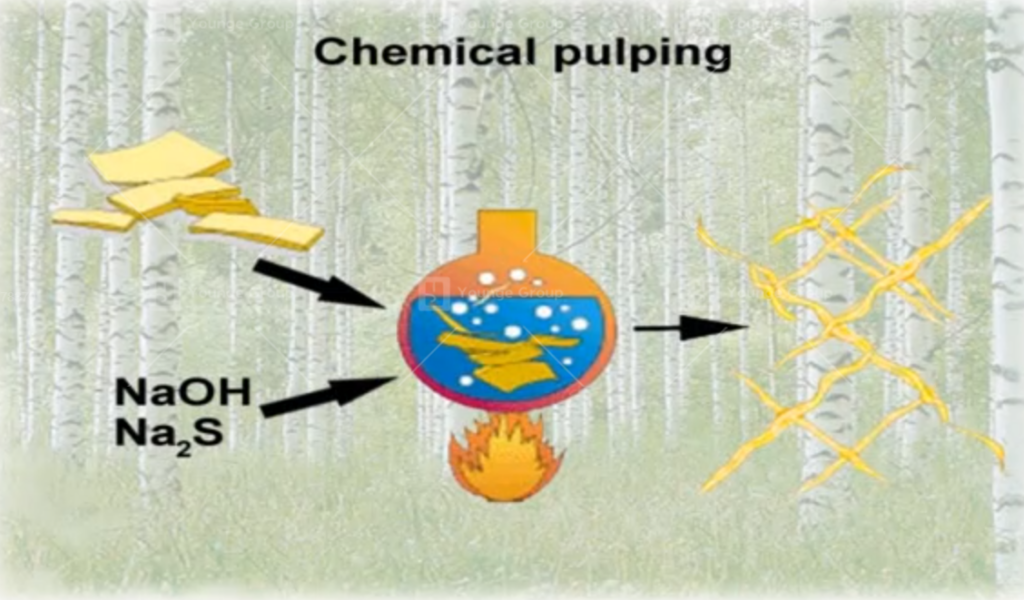
Chemical pulp preparation is feeding wood pieces into the system for cooking to produce unbleached pulp, then oxygen de-lignification proceeds to increase the whiteness, and white pulp can be obtained after being whitened.
The essence of chemical pulping is to allow chemical solutions to react with plant fibers at high temperatures to dissolve as much lignin in the intercellular layers and cell walls as possible, thereby dissociating the raw materials into pulp.
This results in high quality pulps, which can be used for printing and writing paper. However, the yield of chemical pulping is generally lower than other methods, resulting in more expensive pulps.
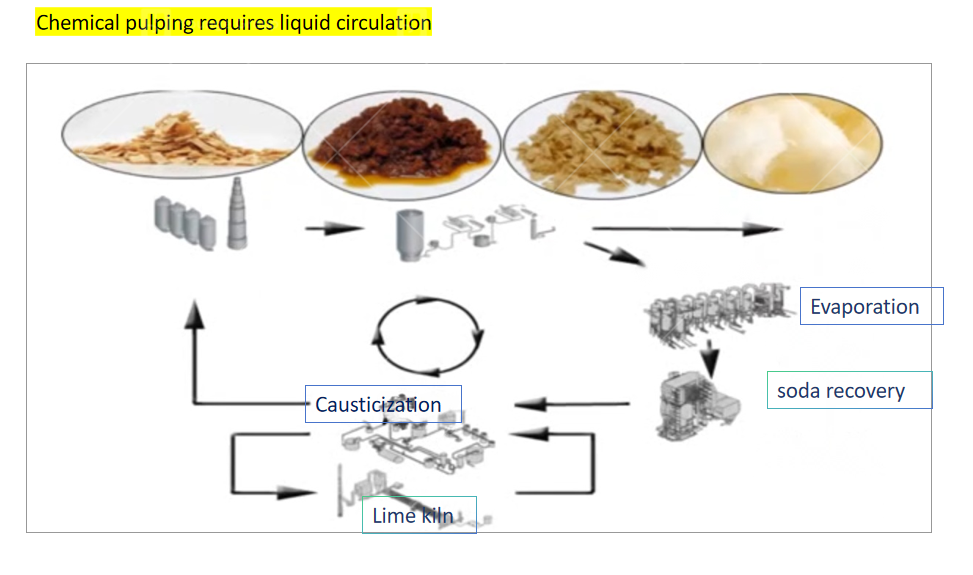
For chemical pulping, cooking liquor should be recycled to reduce pollution.
Modern chemical pulping mainly refers to the alkaline process for more than 90%.
The pulping technologies include continuous and displaced cooking.
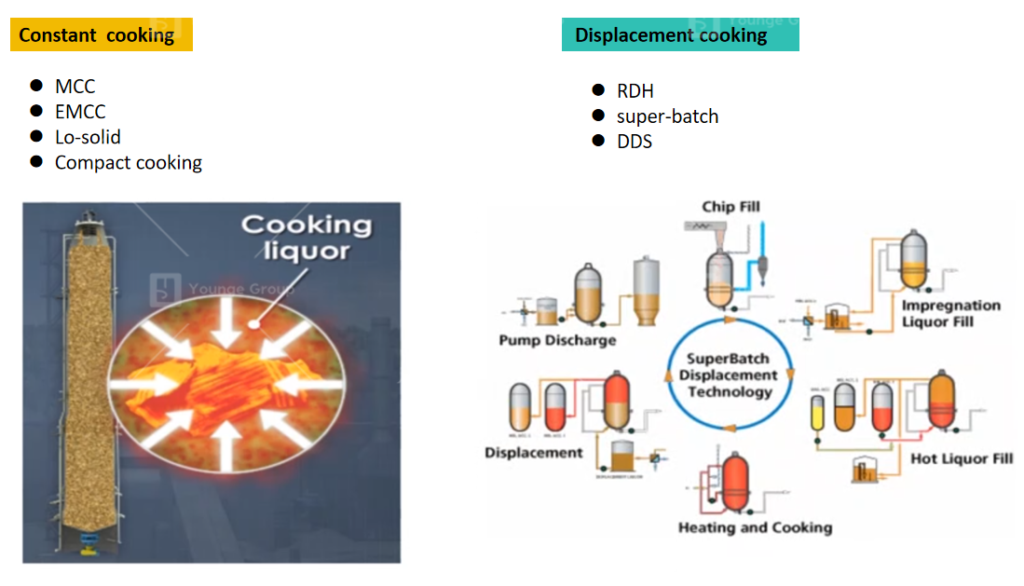
- Continuous cooking: MCC, EMCC, Lo-solid, and compact cooking)
During continuous cooking chips and chemicals are fed from the top and removed from the bottom of the digester. Digester is divided into zones, in which different phases take place.
- Displaced cooking: RHD, EMCC, DDS.
During the batch process, the pulp is cooked phase by phase in each digester. There are several digesters in a digester house.
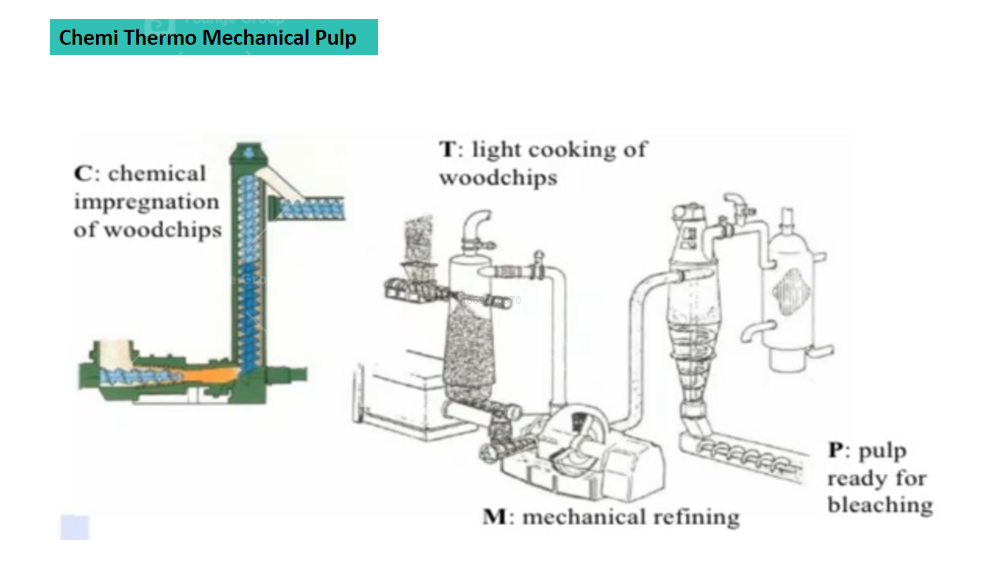
Chemical thermo mechanical pulping proceeds with chemical pre-impregnation and slight heat, then pulping grinding, after being whitened, the pulping is what we call BCTMP.
Development trend of pulping
The following requirements should be fulfilled:
- High yield rate
- Nature color paper making
- Low discharge of system
- Low energy consumption of the system
- High quality of pulp
In terms of process
- Sulfate pulping
- Soda-anthraquinone process
- Chemical mechanical pulping
- mechanical pulping
In terms of technology
Chemical pulping
Continuing cooking: Double towel for Large-scale pulping plant,
Displacement cooking: medium and small-scale pulping plant.
Mechanical pulp, the main technologies: BCTMP& APMP.


