In the pulping and papermaking process, the pressure screen is a key screening equipment. Its main function is to remove impurities in the pulp, improve paper quality, reduce energy consumption in the production process, and help extend the service life of the equipment.
The operating condition of the pressure screen will directly affect the stability of the entire production line.
Today, let’s discuss the causes of common pulp hanging phenomenon of the pressure screen in the flow section and the corresponding improvement measures.
The following are schematic diagrams of the pulp hanging phenomenon of the inner flow screen basket and the outer flow screen basket.
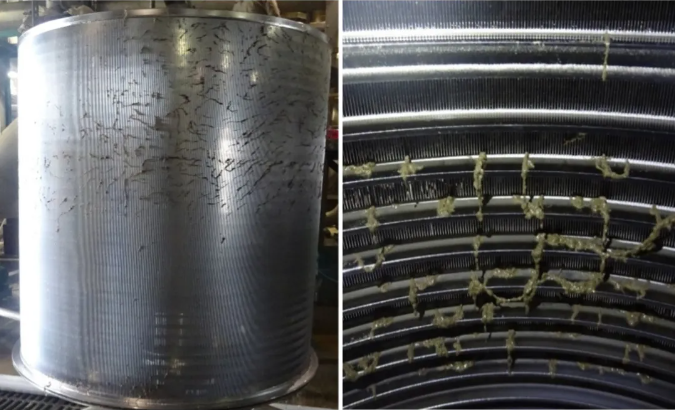

Inflow screen basket

outer flow screen basket
Effects of screen basket hanging pulp
There are four major effects when the flow pressure screen basket hangs pulp:
When the fiber flocs hanging on the good pulp side of the screen basket break and enter the pulp box and go online, causing pulp throwing and paper breaking, it will:
- Increase the number of unplanned shutdowns;
- Affect product quality;
When the fiber flocs hang on the working surface of the screen basket, it reduces the normal working clearance and increases the resistance of the rotor when rotating, which will:
- Shorten the equipment life;
- Increase the equipment operation load;
Causes of pressure screen pulping and solutions
What are the main causes of the pressure screen pulping problem in the papermaking flow section? And how to solve it?
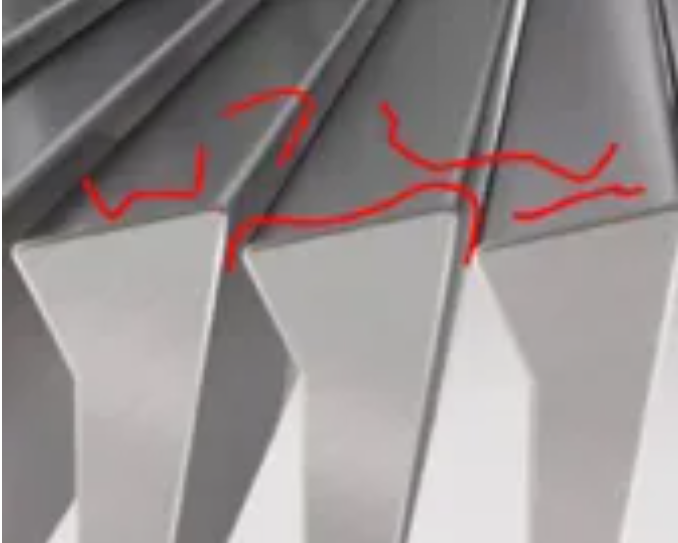
1.High long fiber content in raw materials
When the long fiber content is too high and the fiber length is greater than the width of the screen bars used in the screen basket, the fibers will form bridges between the screen bars and cannot pass through the screen gaps normally, which will increase the probability of fiber hooking and bridging at the same position. As shown in the figure below, the red color is the simulated fiber length.

Solutions:
- In the initial stage of pressure screen basket selection, fully consider the changes in paper types and the ratio of raw materials used;
- The width of the selected screen bar must be greater than the fiber length of the long fiber to avoid fiber bridging.
2.The screen basket and rotor blades are bumped/worn
When the slurry reaches the flow system, it is relatively clean, but the flow screen will run for a long time, and the screen basket and rotor will also be worn to varying degrees, and need to be replaced or repaired regularly.
The wear of the screen basket and rotor is shown in the figure below:

The screen bars are bumped and deformed

The rotor blades are bumped and worn
After the screen bars collide with each other, they extend and deform, forming a bridge with the adjacent screen bars. This position becomes closed, and the fibers are easily caught here, causing chain flocculation.
After the rotor blades collide and wear, the gap between the area with greater wear and the screen basket at the same position becomes larger. When the rotor rotates, the pulse in this area will decay, and the pressure and backwashing capacity of the slurry will decrease, which may cause the slurry to not pass through the screen gap sufficiently, causing fiber retention and flocculation.
The hard impurities that cause the screen basket and rotor blades to collide and wear mainly come from two locations:
(1) The breakage of the grinding teeth of the grinding disc used in the mill, and the broken grinding teeth enter the flow system;
(2) The shedding of welding slag accumulated in the original pipeline.

Solutions:
- When the machine is shut down, the wear of the screen basket and rotor should be checked regularly; spare parts should be replaced in time if wear occurs;
- Regularly check the gap between the rotor blade and the screen basket. If the local gap is too large or too small, adjust it in time. The rotor type used should try to use the rotor blade with adjustable gap to facilitate adjustment; the fixed rotor blade rotor has a welded connection between the rotor and the main body, which cannot be flexibly adjusted according to the on-site use (this is its disadvantage).
- When checking the screen basket and rotor, if the broken metal particles accumulated in the rotor are found, they should be cleaned in time to prevent them from falling off and causing further wear on the screen bars and rotors.
3.Design flaws
(1) Rotor design defects
As shown in the figure below, when the pressure screen model is relatively large, the rotor will basically adopt a two-stage or multi-stage design. There will be a non-overlapping area in the middle of the rotor blades. In order to deal with the problem of no rotor pulse in this area, the area is generally connected with a blind flange.
After long-term market testing, it is found that the blind flange cannot effectively avoid the problem of slurry accumulation in this area. As shown in the figure below (right), it will cause the problem of fiber flocculation accumulation around the screen basket.

Solution:
The rotor blades are optimized, and the corresponding upper and lower blades are partially lengthened in the middle position to perform similar gap compensation without leaving a gap in the middle. After the front and rear blades rotate, they can cover the blind flange area to meet the corresponding pulse requirements.
(2) Wrong selection of rotor linear speed
When dealing with different pulps and different types of pressure screens (inner flow & outer flow & inner and outer double-layer), we choose different linear speeds of the pressure screen rotor. The wrong rotor linear speed will not only make the entire pressure screen unable to operate stably, but also cause the motor load to increase and the pulp to concentrate and accumulate in the screen body, causing a series of problems such as fiber hanging pulp flocculation and screen sticking.
Solution:
Consult the pressure screen manufacturer for standard guidance on the linear speed of the rotor.
Optimizing treatment with perforated screens
In addition to the above-mentioned measures to solve the problem of slurry hanging on the screen basket, corrugated perforated screens are also being used in the market for optimization.
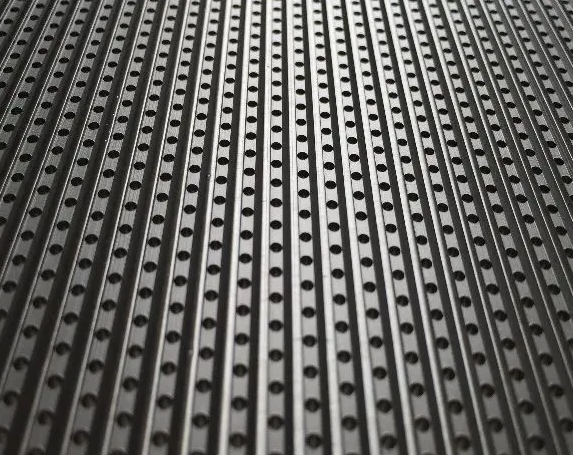
Corrugated hole screen plate
The hole screen can improve more than 90% of the fiber flocculation and pulp hanging problems, thanks to the flexible arrangement of the hole spacing of the screen basket aperture, and the distance between the holes is far, so the fibers cannot form bridges close to each other. In addition, the surface of the hole screen is also electropolished accordingly to achieve a certain finish standard, and the pulp hanging problem will not be caused by the rough surface.
The hole screen has a longer service life than the slot screen, but its only disadvantage is that the aperture is larger than the slot screen (the commonly used flow section screen basket hole screen is 1.4-1.8mm vs the slot screen is 0.25-0.4mm). Some round fine particle impurities will enter the subsequent process through the screen holes, causing some paper quality problems. For paper types with strict requirements on paper quality, use the hole screen with caution to solve the fiber hanging problem.


