How to improve paper burst resistance?
There are many factors that affect paper burst resistance, which can be basically summarized in3 points as follows:
- The decisive influence of the raw material’s own characteristics (fiber type and its characteristics);
- The significant influence of pulping process and its control;
- The subsequent processing and performance improvement of paper sheet structure by various process equipment (including headbox, forming section, pressing section, drying section, sizing section, coating section and calendering section).

Raw material properties are the determining factors for paper burst resistance
The raw material of paper is fiber, and its length, coarseness, thickness, fiber strength and toughness have a decisive influence on burst resistance. Generally speaking, the longer the fiber, the tighter the interweaving between fibers and the more interweaving points; the higher the fiber strength and toughness, the better the strength and burst resistance of the paper. Generally, coniferous wood fiber is superior to hardwood fiber. The addition of high-strength fiber (including the currently recommended chemical fiber) can significantly improve burst resistance and strength, but it will also increase costs.
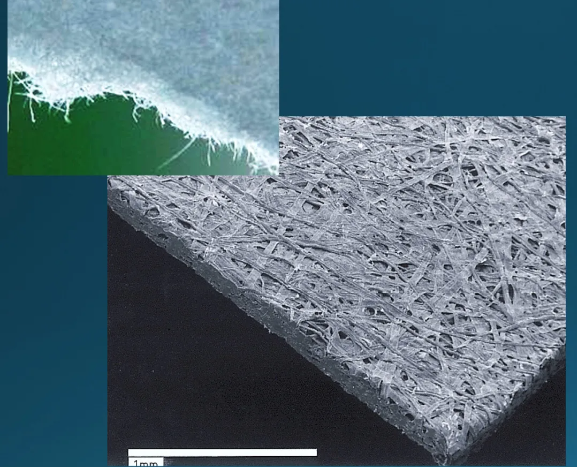
The significant impact of pulping process on burst resistance
Reasonable pulping and beating degree have a very important impact on the burst resistance of paper. The principle of pulping is to use physical methods to treat pulp fibers in water. During the pulping process, in addition to mechanical shearing, rubbing, extrusion, dispersion and combing, the fiber cell wall will also undergo displacement, deformation and rupture, and at the same time absorb water and swell to produce fine fibers. This makes the pulp soft and plastic, and the surface area increases. At the same time, the hydroxyl groups in the cellulose molecular chain increase, and the opportunities for hydrogen bonding increase, which improves the bonding force between fibers. The higher the beating degree, the higher the degree of fiber fibrillation, resulting in more points of fiber arrangement and interweaving in the later stage. The closer the interweaving, the better the burst resistance of the paper.
However, excessive beating will destroy the fiber structure, reduce the strength and toughness of the fiber, and increase energy consumption, which will eventually damage the overall performance of the paper. Therefore, the beating degree must be strictly controlled to ensure that the fibers are fully dispersed and refined without excessive damage.
Influence and improvement of subsequent equipment
Other equipment in the subsequent stage interferes with the arrangement of pulp fibers, including headbox, wire, press, drying, sizing, coating, calendering and other equipment. The operating parameters and design features of these subsequent equipment will also affect the fiber arrangement and structure of the paper, thereby indirectly affecting the burst resistance.
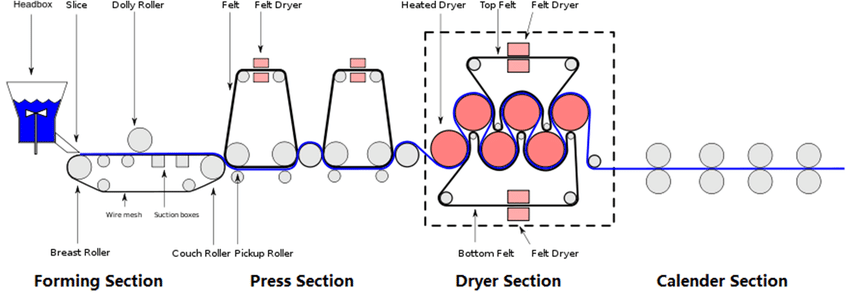
Headbox and Forming Section
The pulp after beating is formed by the headbox and forming net through the flow conveying system. Under normal circumstances, the better the uniformity, the tighter the fiber interweaving, and the more uniform the dispersion, the higher the strength and tear resistance of the paper.
During the web process, the fibers are more horizontally arranged, including multi-directional interweaving in CD and MD directions. The more dispersed the fibers are, the tighter the interweaving is, the higher the uniformity and tear resistance of the paper. The arrangement of the fibers will affect the uniformity and tear resistance.
It should be noted that uniformity and tear resistance are two different concepts.
Reasonable interference of the headbox, such as the headbox with a bleaching sheet installed, can generate shear force on the paper-forming fibers, so that more fibers are arranged and interwoven in the horizontal direction. The use of the shaking device can cause the fibers to deflect laterally and balance the high and low points of sizing, thereby improving uniformity and enhancing burst resistance.
However, although the turbulence generated by the headbox can break up the aggregated fibers and improve uniformity, it has a negative impact on burst resistance. This turbulent disturbance persists after the pulp flies off the lip area. Although it continues to improve the uniformity, it will also deteriorate the burst resistance.
Because in the turbulent state, more upright fiber arrangements will appear in the pulp layer, reducing the interweaving of the fibers in the flat direction, resulting in a reduction in the horizontal fiber arrangement. More upright fiber arrangements are likely to reduce the strength of the paper and cause paper breaks. However, for multi-layered headboxes and multi-layer screen paper machines, upright fiber arrangements can improve the interlayer bonding strength (commonly known as Z-axis strength), but will deteriorate the burst resistance.
Including the turbulence formed by the turbulence generator and the turbulence generated on the inner side of the upper lip plate, under the premise of ensuring the uniformity of the paper, the laminar state should be as close as possible to the moment the pulp flies off the lip, which is beneficial to the burst resistance.
In addition, if the landing point is too close or the flying pulp injection angle is too large, some fibers will be arranged upright, or rebound upright after touching the forming mesh, which is not good for the burst resistance of the paper.
Pressing section
After the paper is formed, the fibers are squeezed through the pressing section to make the fibers denser and tighter, and to increase the interweaving points between the fibers. Higher line pressure can improve the pressing effect, but too high line pressure may destroy the fiber characteristics and cause problems such as fiber fracturing.
Drying section
The drying section is a very important link in the papermaking process, which can quickly dehydrate the paper and increase its strength. During the drying process, the water molecules in the paper are evaporated, the connection points between the fibers are better supported, the paper fibers shrink, become denser and tighter, and thus improve the strength of the paper. However, too high drying temperature and time can also be counterproductive. In particular, high-temperature drying can cause the water in the fiber to evaporate too quickly, causing heat concentration, resulting in hardening, brittle cracking of the fiber, and reduced tear resistance.
Sizing coating
Similarly, the tear resistance of paper will be improved after sizing coating. By coating the paper surface with sizing material, not only the water resistance, ink absorption, erasability and wear resistance of the paper are improved, but also the strength and stability of the paper are enhanced.
Sizing can form a protective film on the surface of paper, reduce water penetration, and improve wet strength; at the same time, it can enhance burst resistance and tensile strength to ensure stability during printing. In addition, sizing can stabilize the moisture content inside the paper. Too high or too low moisture content will reduce burst resistance. Both internal sizing and surface sizing can effectively improve paper performance. Some multi-layered papers may add adhesive glue between layers to achieve similar effects.
Calendering section
Finally, the paper can be slightly improved in burst resistance after being calendered by the calender. The calendering process can effectively remove the air inside the paper, making the fibers more interwoven and arranged more closely, making the paper surface smoother, and improving burst resistance.
Conclusion
To improve the burst resistance of paper, multiple factors need to be considered comprehensively. Raw materials and pulping process often play a decisive role, and for some papers, the influence can reach more than 80%. The flow system, headbox, forming section, press section, drying section, and subsequent links such as sizing, coating, and calendering account for about 20% of the influence. However, this does not mean that optimizing subsequent equipment can directly improve the burst resistance by 20%.
To obtain excellent burst resistance, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of the overall production process and rich practical experience.
In addition, adding wet strength agents, dry strength agents and other chemical additives can further improve the burst resistance.


